Innovation in mitigation technologies is seen as a critical contributor to achieving the ambitious GHG reduction goals of countries outlined in the Paris Agreement. The CARISMA project has analysed collaboration initiatives from governments, industries, and regions, each with different characteristics, to identify criteria for effective collaborations between the EU and emerging countries. The main finding of the analysis is that there is no unique pattern that could correspond to every good practice of collaborations.
Research - Universities & knowledge centers
Transition pathways are compared to the land use domain of the Netherlands and Portugal. The land use domain analyses land systems and the changes within them and typically involves the analysis of land cover and land use. 4 main regimes were identified, three of which are common to both: agriculture, nature, and urban, and one which is different for each. The Dutch and Portuguese niches under study are all examples of regime transformation niches.
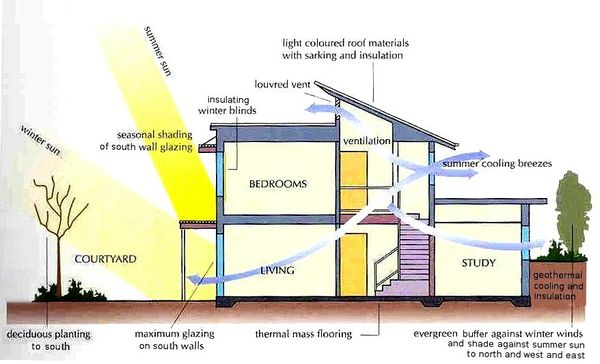
Models are tools which help to assess the positive and negative impacts of a low-emission pathway for the country. Interview questions formed the basis for a series of model runs to obtain a better understanding of the implications of the energy efficiency pathway in Poland. The goal of the model run was to shed light on the macroeconomic impacts of investment in energy efficiency in Poland in the built environment.
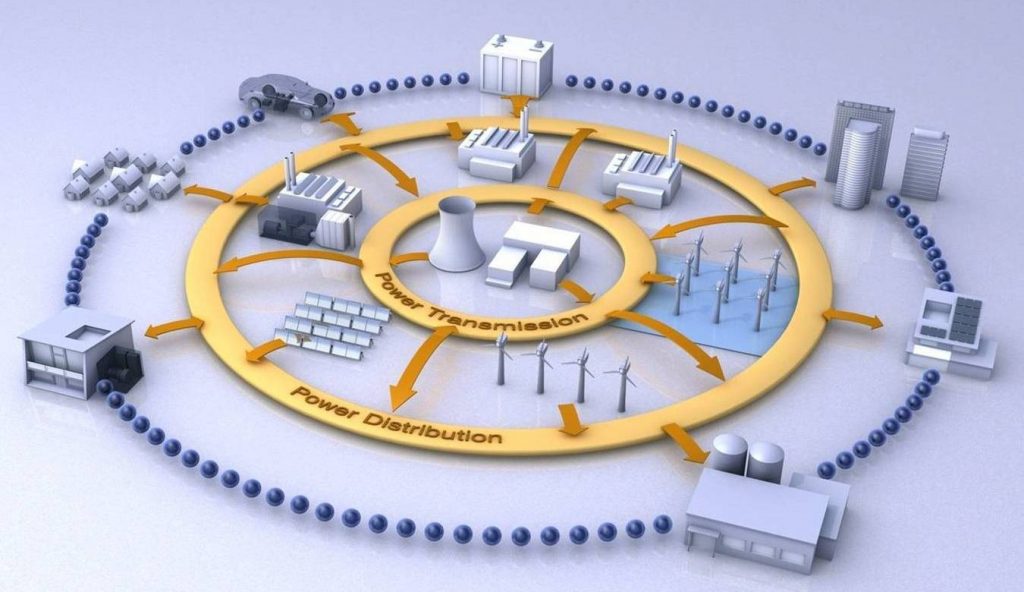
Institutional, economic, and social contexts influence the formulation and implementation of climate policy instruments. Three categories of contextual factors that are especially relevant to climate change mitigation in EU policymaking: institutions and governance, innovation and investment and attitudes, behaviour, and lifestyle. Different factors or conditions may facilitate or hinder effective policy implementation as so much depends on the institutional, economic, and social contexts. In addition, not only international pressures but also local barriers.
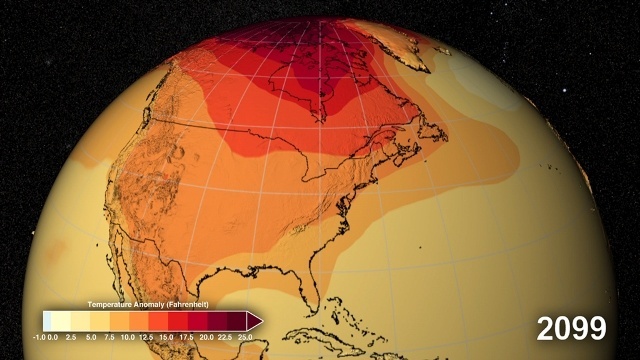
Europe has taken a leading position in relation to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by adopting ambitious policies for the development and diffusion of renewable energy technologies. However, research and development (R&D) in new technologies is increasingly taking place on a global scale. This increasingly also involves the relocation of R&D and value-adding innovative activities to emerging economies, such as China, India and Brazil, by multinational companies (MNCs) from Europe.
In the PATHWAYS project, empirical transition pathways have been compared to ideal-type transition pathways. All analyses use the multi-level perspective (MLP) to explain similarities and differences between the different countries. One of the domains considered is land-based passenger mobility, with empirical transition pathways from the United Kingdom and the Netherlands.
Research often focuses on creating and modelling hypothetical scenarios. However, public knowledge and opinions are crucial for the successful uptake of research findings. In this article, we explore how quantitative tools are used for producing scenarios, whereas qualitative tools are used to identify stakeholder preferences.
In this article, heat energy transition pathways in the UK, Germany and Sweden have been compared by evaluating empirical to ideal scenarios. Heat energy transition is the core of the energy transition, as heating is currently the most energy-intensive activity in Europe.
In this article, we analyze empirical and ideal scenarios for electricity system transitions in Germany and the UK through Multi-Level Perspective (MLP).
There are many case studies on local and regional transitions. Until now, an overview of such case studies was missing. The EU-funded PATHWAYS project has created a database that allows for sharing information from previously done European case studies, in order to foster the reuse of the knowledge gained in previous studies.