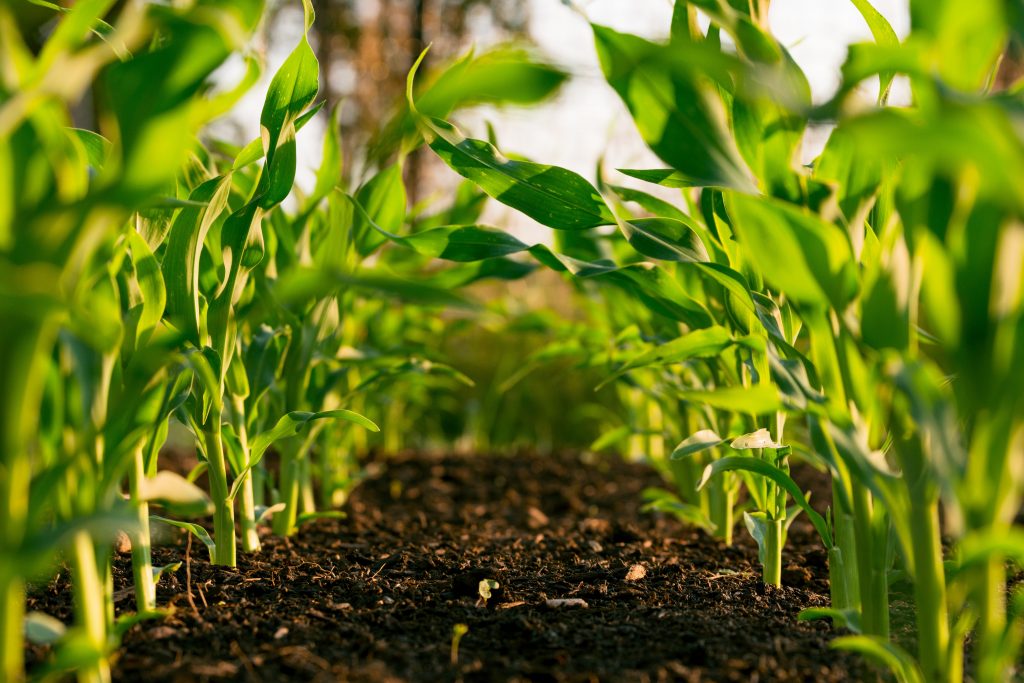
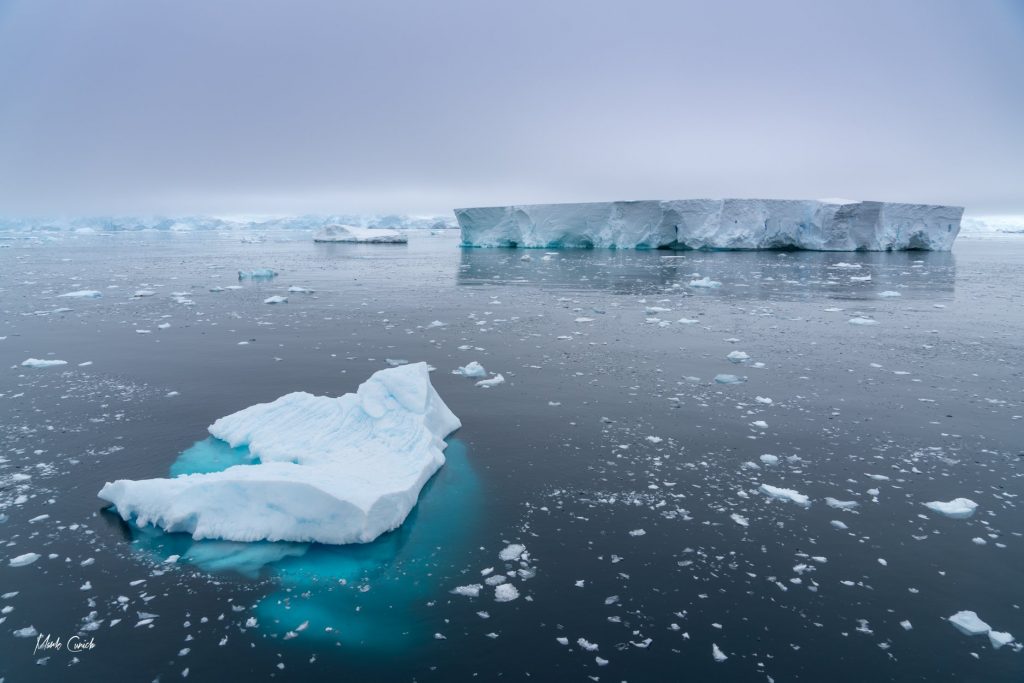
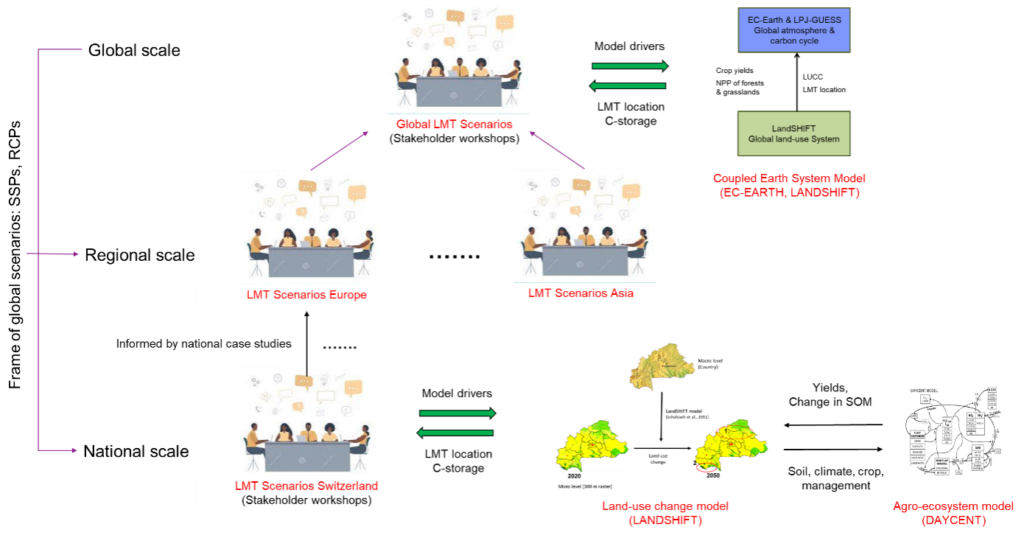
At LANDMARC, we are developing methods and instruments that non-researchers can use to reliably estimate how different land-use practices contribute to climate change mitigation. In our view, this can only be done by bringing in local knowledge at every stage of the research process. Here’s why.
Mobilising research and fostering innovation
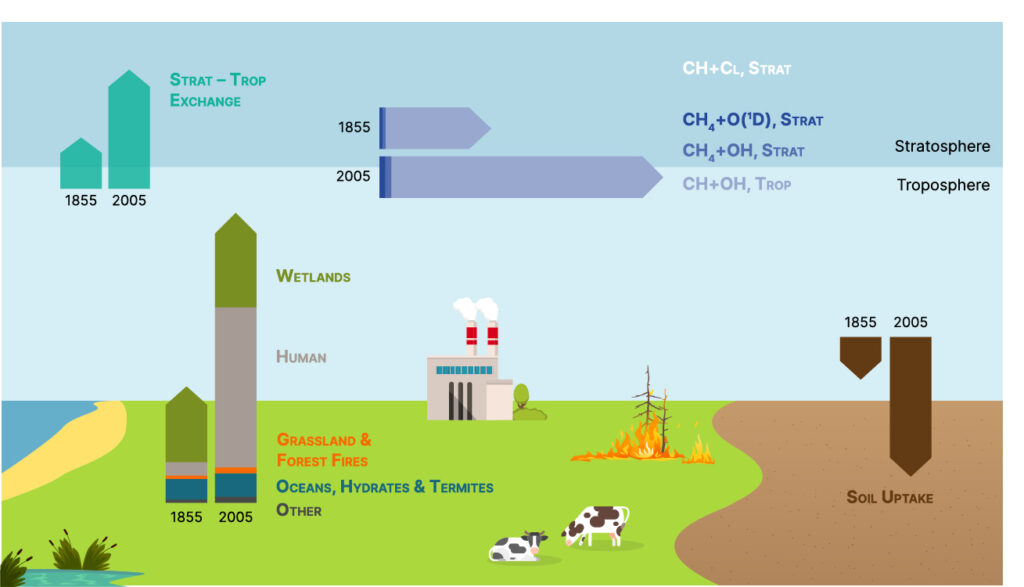
The first fully-coupled methane emission driven Earth system model capable of simulating the impact of anthropgenic forcing on natural environments, as well as the impact of methane emissions and mitigation strategies on air quality.
In the first year of LANDMARC, Bioclear earth led the soil sampling of 2 case studies in the Netherlands related to agroforestry and paludiculture, one case study in Portugal related to pasture and one case study in Kenya related to soil management.
The EU-funded Beyond EPICA project set up a camp at Little Dome C in East Antarctica, with the aim to obtain quantitative, high-resolution ice-core information on climate and environmental changes over the last 1.5 million years
From COP26 in Glasgow, the adoption of comprehensive accounting rules for the international transfer of carbon market units is the most important achievement however it is not in international climate negotiations. ‘Clean Development Mechanism’ or ‘CDM’ allows emission reduction projects to earn certified emission credits, but there are questions if the Article 6 rules are good enough to provide the necessary framework.
There are uncertainties how emission cuts will affect chances of staying with in 1.5°C warming dependent upon how the climate system responds. By looking at the science and models behind COP26 headlines and statements, we better understand our chances of staying within 1.5°C and mitigate risk. ZERO IN reported by the CONSTRAIN project highlights issues
In the Paris Climate Agreement, the five-yearly Global Stocktake (GST) plays an essential role. GST is used to monitor the implementation and progress of the Paris Agreement. Applying the concept of governance functions of international institutions, the policy brief derives the key recommendations to contribute to understanding.
EU- funded DEEDS project gives recommendations on Research and Innovation (R&I) aimed at decarbonisation of the EU economy and society and are relevant to the EU Green Deal.
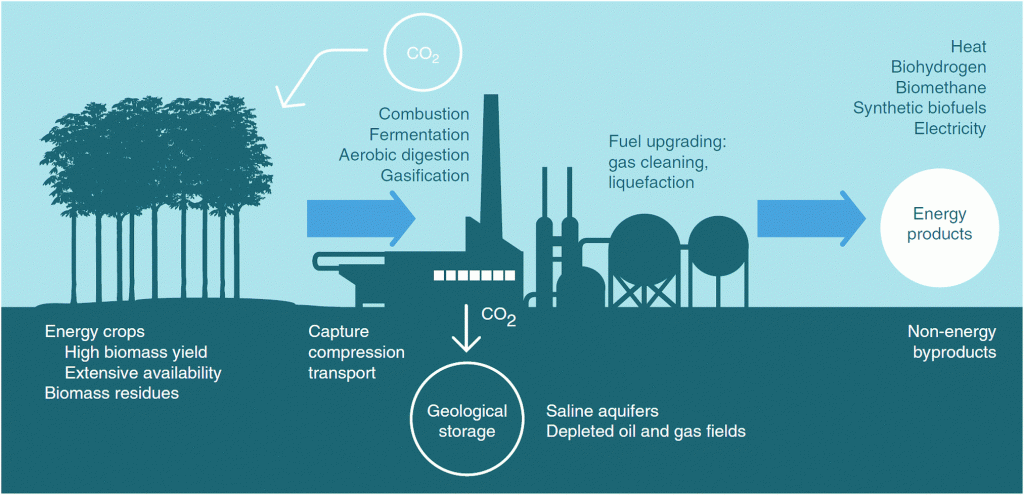
Key in the process for low-carbon transition is a transformation in all sectors and regions and the incorporation of new technologies and practices. Research and Innovation (R&I) is key in the development and successful uptake of clean technologies and focuses on three key non-mature technologies, CCS, advanced biofuels, and batteries for electric vehicles, as well as on energy efficiency measures explained in the report.
The transition to low carbon practices requires incorporating new technologies and practices, with Research and Innovation (R&I) being key in developing. Optimal R&I strategies increase the feasibility of ambitious climate stabilization targets by lowering carbon prices and mitigating costs.