The drastic growth of cruise tourism in the world, while potentially beneficial for economic growth in local communities, also brings concerns regarding environmental impacts. This research used the port of Ísafjörður, Iceland, a growing hotspot destination for cruise ships, as a case study to aid in understanding the potential environmental impacts from cruise ships.
Policy
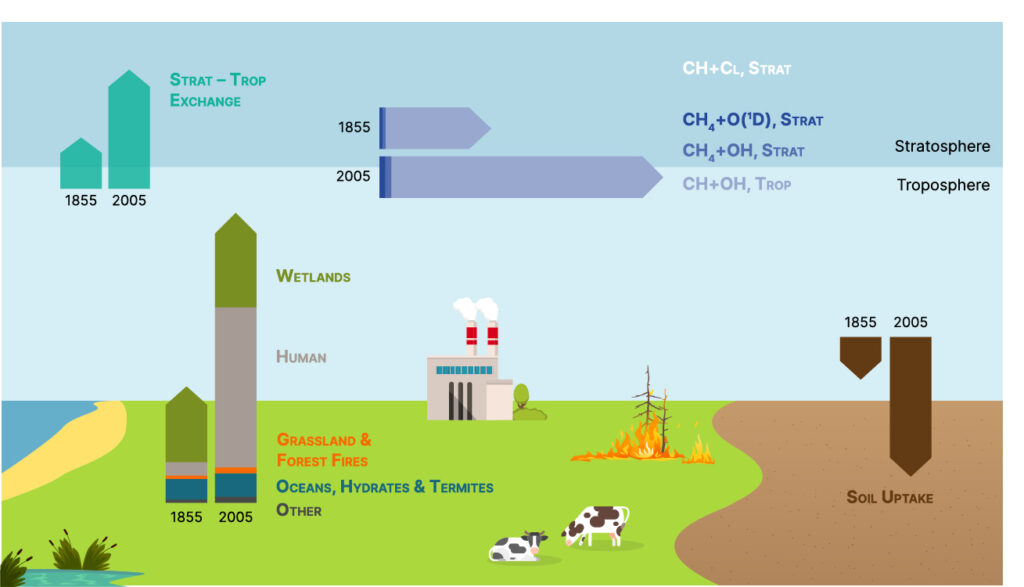
The first fully-coupled methane emission driven Earth system model capable of simulating the impact of anthropgenic forcing on natural environments, as well as the impact of methane emissions and mitigation strategies on air quality.
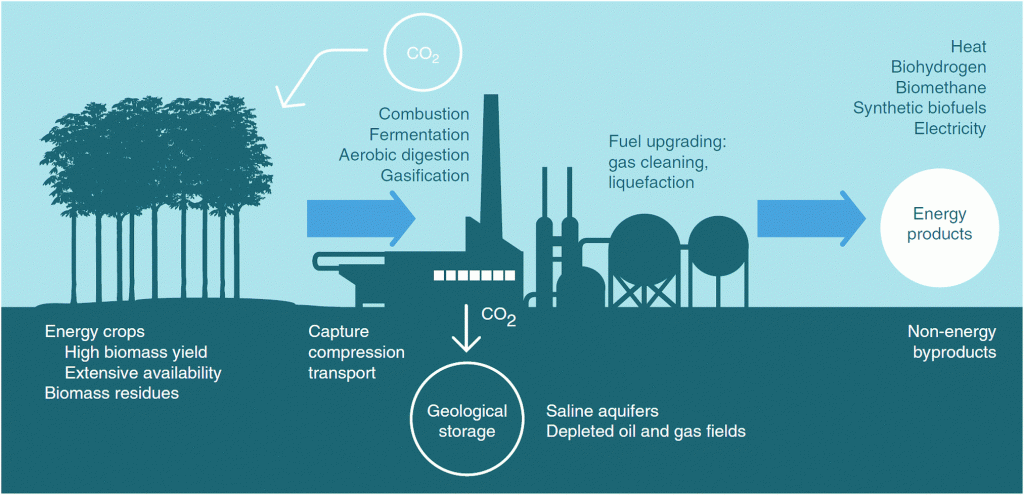
In a time of increasing demand for the earth’s limited resources, the GoNEXUS project develops solutions for more efficient and sustainable resource management. It does so through a holistic approach to how the resources interplay rather than by examining each one of them individually.
Using Organigraphs to Map Disaster Risk Management Governance in the Field of Cultural Heritage.
Louis J. Durrant, Atish N. Vadher, Mirza Sarač, Duygu Başoğlu and Jacques Teller
The latest ZERO IN report from the CONSTRAIN project dives into the science set out in the recent Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change assessments. It investigates what our climate future could look like by 2050, depending on whether we take action in line with the Paris Agreement, or decide to follow current national policies and plans which still largely lack the action and ambition needed to stop global warming.
This briefing explores the questions raised during the first ESM2025 policy forum and details the contribution of ESM2025 to various policy-relevant topics.
New study on the impacts of wildfire emissions on fine particle air pollution in the western US until the end of the 21st century, under different climate change scenarios.
This work highlights the fact that when committing to a particular level of future warming, we are also committing to a particular level of fine particle air pollution. This has to be taken into account when considering mitigation and adaptation strategies.
The Global Stocktake assesses the world’s collective progress towards achieving the purpose of the Paris Agreement and its long-term goals.
From COP26 in Glasgow, the adoption of comprehensive accounting rules for the international transfer of carbon market units is the most important achievement however it is not in international climate negotiations. ‘Clean Development Mechanism’ or ‘CDM’ allows emission reduction projects to earn certified emission credits, but there are questions if the Article 6 rules are good enough to provide the necessary framework.
There are uncertainties how emission cuts will affect chances of staying with in 1.5°C warming dependent upon how the climate system responds. By looking at the science and models behind COP26 headlines and statements, we better understand our chances of staying within 1.5°C and mitigate risk. ZERO IN reported by the CONSTRAIN project highlights issues