EU- funded DEEDS project gives recommendations on Research and Innovation (R&I) aimed at decarbonisation of the EU economy and society and are relevant to the EU Green Deal.
Mobilising research and fostering innovation
Economic growth has been a priority for the European Union (EU) since its creation. The Paris Agreement targets will not be reached by technological and policy measures alone, businesses need to contribute and commit to the decarbonisation journey. The Business Guide calls to policymakers and businesses to move decarbonisation strategies from words to reality.
DEEDS’ knowledge base constitutes of two components: the scenario explorer and the technology database and intends to reach out to a broader audience and academia who could deliver deep and rapid reductions in emissions. This may help stakeholders to access detailed information about expected European emission limits, technology markets and energy prices, to develop strategies and understand the market potential for technologies consistent with decarbonisation pathways.
The European climate change strategies key element is the transition of the energy system towards a more sustainable energy supply, and the decarbonisation of the electricity sector through the deployment of renewable energy technologies. Concentrated Solar Power (CSP), as a dispatchable renewable energy technology combined with thermal energy storage, could contribute to the deep decarbonisation of the European Energy system by providing sustainable electricity and adding to system flexibility.
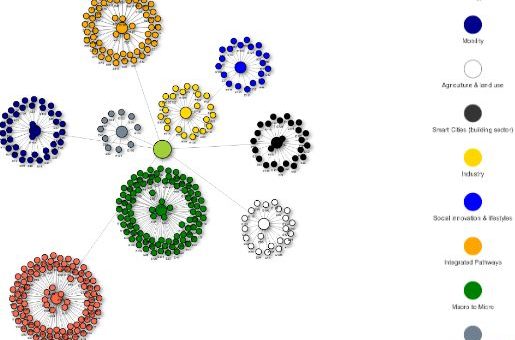
The Paris Agreement requires a global decrease in Green House Gas emissions by 2050 which requires input from cities. Research and Innovation (R&I) in European cities is described in this paper and explains the critical R&I actions in cities based on three pillars.
The DEEDS (Dialogue for European Decarbonisation Strategies) invited European and non-European experts to be part of a scientific group that will support the European Decarbonisation Pathways Initiative (EDPI). A database has been created for experts to join DEEDS.
Permafrost occupies 24% of the Northern Hemisphere’s land surface and is warming faster than the global average, thus melting permafrost: which has significant implications for efforts to control climate change. Quantities of organic carbon become available: permafrost contains twice as much carbon as in the atmosphere. The presence of permafrost carbon requires that the reduction of fossil fuel and industrial CO2 emissions needs to be greater and occur earlier.
New frameworks and tools are provided by TRANSrisk to manage climate change policy and are designed within the context of national case studies. Technological Innovation Systems (TIS) approach is used to explain the rate and nature of technological change in the case studies. The TRANSrisk project has two additional sectors alongside the four conventional circular economy sectors. A cross-sectoral approach is used to explore synergies and conflicts and risks and uncertainties of various innovative low
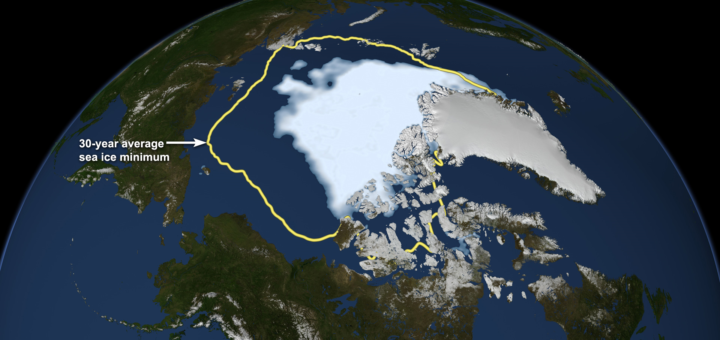
Arctic sea ice decline in recent decades is one of the most visible indicators of global warming. The sea-ice albedo feedback is an essential impact of sea ice melt, which amplifies Arctic temperature change. In this study, an optimal path for fossil fuel and industrial CO2 emission reduction is sought. Devoting more resources to mitigation implies a decrease in consumption and investment, implying a loss in net welfare.
Innovation in mitigation technologies is seen as a critical contributor to achieving the ambitious GHG reduction goals of countries outlined in the Paris Agreement. The CARISMA project has analysed collaboration initiatives from governments, industries, and regions, each with different characteristics, to identify criteria for effective collaborations between the EU and emerging countries. The main finding of the analysis is that there is no unique pattern that could correspond to every good practice of collaborations.