The study focuses on the planning phase of nature-based solutions in cities, in which trade-offs have to be made between different options, such as the design, effectiveness, financial contributions from residents or participatory options. Based on the UPSURGE survey and choice experiment, the aim is to assist public participation processes in various countries, help planning teams define priorities and design governance measures which ensure long-term dedication to development plans.
Good health and well-being
The Generic Quantitative Risk Assessment report described implementation of a site soil survey and consequent contamination remediation action for the Lower Botanic Gardens (Belfast, UK). The exploratory site investigation was undertaken between October-December 2022, and comprised excavation of 28 soil samples and subsequent laboratory analysis for a common contaminant suite. Results confirmed contamination distributions linked to historical industry. Risk remediation actions were proposed for features with different levels of soil exposure.
The Preliminary Risk Assessment desk survey was produced prior to soil investigations on the Lower Botanic Gardens (Belfast, UK). Planning records revealed little site development over the past 200 years, but identified multiple local historical industry-linked contaminant sources that could contribute to soil contamination. Community growers and site developers were considered most at risk from ingesting or inhaling any contaminated site soil dusts.
Air pollution is a growing concern that continues to strongly affects cities worldwide, posing significant threats to both human health and the environment. Nature based solutions is an innovative approach that harness the power of nature and its inherent ability to filter, absorb and mitigate pollutants. In the frame of the Upsurge project, different NBS are being implemented to study their benefits with a focus on air quality and climate remediation.
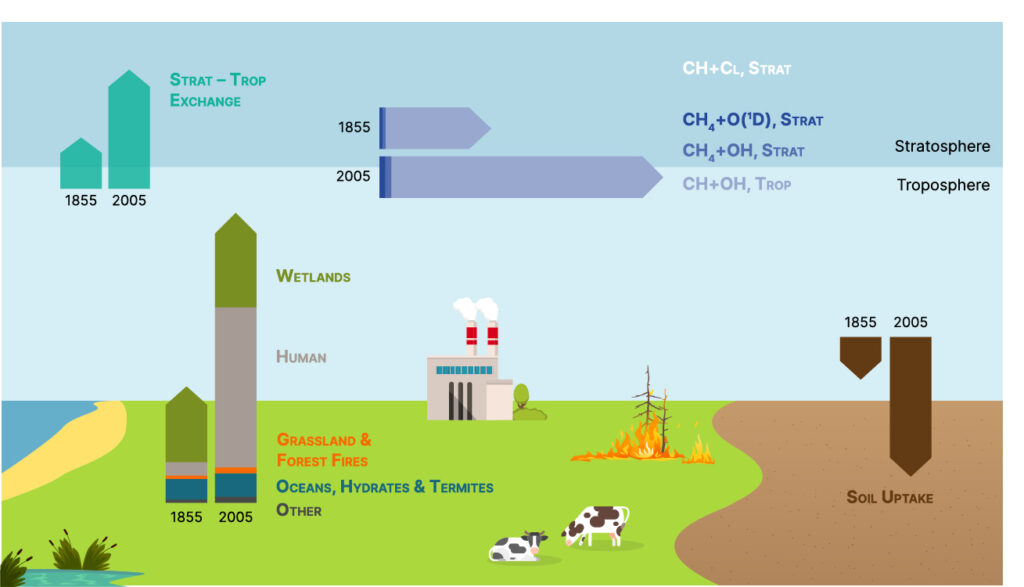
The first fully-coupled methane emission driven Earth system model capable of simulating the impact of anthropgenic forcing on natural environments, as well as the impact of methane emissions and mitigation strategies on air quality.
New study on the impacts of wildfire emissions on fine particle air pollution in the western US until the end of the 21st century, under different climate change scenarios.
This work highlights the fact that when committing to a particular level of future warming, we are also committing to a particular level of fine particle air pollution. This has to be taken into account when considering mitigation and adaptation strategies.
A significant proportion of Eastern Africa is a relatively poor with a predominately rural population and lack access to modern energy services. Reliance on traditional biomass has created severe problems for both the environment and the health of the population: improved access to cleaner fuels would solve this and achieve multiple policy goals. The Global Change Assessment Model (GCAM) is utilised to simulate future scenarios. The study suggests the optimal subsidy policy implementation and recommendations.