The European climate change strategies key element is the transition of the energy system towards a more sustainable energy supply, and the decarbonisation of the electricity sector through the deployment of renewable energy technologies. Concentrated Solar Power (CSP), as a dispatchable renewable energy technology combined with thermal energy storage, could contribute to the deep decarbonisation of the European Energy system by providing sustainable electricity and adding to system flexibility.
Articles
Biomass and its demand are growing for multiple uses, such as food for humans and livestock, biofuels, and biomaterials. So, the competition for the biomass itself, as well as that for the natural and socio-economic resources required for its production, is expected to worsen. The assessment of biofuels as an innovation has shown to be a complex issue and difficult to address with conventional modelling approaches for the following reasons explained in this post.
Individual behaviour could also play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This research explored the impact a range of behaviour changes across mobility, food, heating, leisure, and waste would have on Greenhouse Gas emissions. The results show that individuals’ moderate to rigorous behaviour change in the EU could reduce per capita carbon footprint by 6-16%. Three behavioural profiles were used to estimate emission impact from changes in behaviour: Enthusiast, Conscious and Convenient profiles. The benefits from behaviour change would be significant emission reductions and a variety of co-benefits for public health, land use, and regional ecology.
Different Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) projects has pros and cons for cooperation, so the policy goals in the importing and exporting countries, which partially depend on the context conditions in these countries, should be considered. This post discusses and derives policy implications from CSP projects and how this effects cooperation.
The business case for CSP (Concentrated Solar Power) is difficult to establish for importer countries as well as exporter countries and its impacts. Although the impacts of the energy transition have recently emerged in the geopolitics, CSP, is almost absent from both the academic and the policy-oriented geopolitical literature. This post further discusses the context of policies for CSP deployment by renewable energy cooperation in the EU.
Renewable energy cooperation is expected to play a role to ensure an effective and affordable energy transition in the EU. Besides cost savings in meeting the RES targets, there are multiple factors that determine a Member States’ willingness to engage in a cooperation agreement. Regarding CSP deployment in the past and potential obstacles to the use of cooperation mechanisms, several barriers stand out for cooperation discussed in this post.
There is no uniform format in the energy sector of the EU, although there are some initiatives for regional cooperation leading to intense cooperation between governments in specific parts of Europe. The main asset of regional cooperation lies in the ability of the involved actors to co-ordinate more efficiently. More work is required to address issues related to the further deployment of RES from 2020 to 2030 e.g., the most efficient use of RES potential.
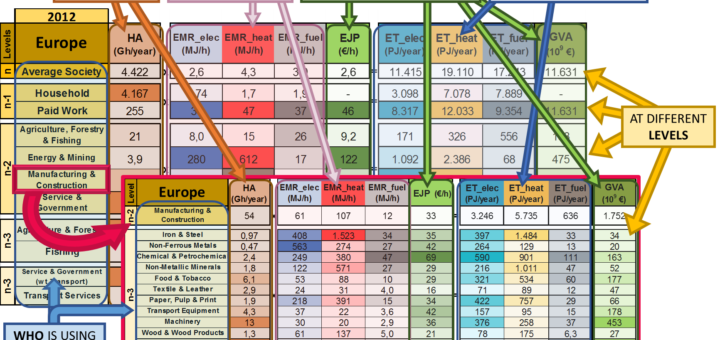
Researchers take a critical look at the use of energy efficiency indicators in energy policy and state the strategy of energy efficiency to save energy is very simple. However, efficiency is problematic to implement. Oversimplification of efficiency measurements can have a detrimental effect on the choice of energy policies. Proposed method unpacks and structures energy input and output information in a meaningful and transparent way by generating a rich multi-level and multi-dimensional information space.
No business model is the same for CSP due to the complexity of projects in terms of engaged actors across the different stages. MUSTEC project team investigated the CSP industry to identify the existing business models and found that the CSP industry has been forced to adjust its original business models. This post further discusses risks and barriers for the CSP industry but also financing opportunities.
Circular economy (CE) is concept that has recently emerged, especially relevant in cities, and that contrasts the linear economic system. Research gaps in the analysis and implementation of circular economy in cities are a significant barrier to its implementation. This paper presents a multi-sectorial and macro-meso level framework to monitor (and set goals for) circular economy implementation in cities based on Porto, Portugal as a case study.