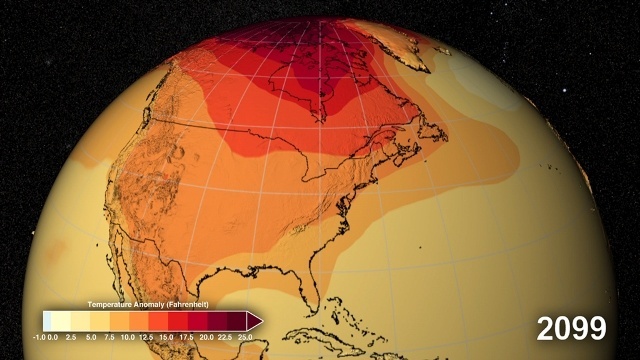
Models are tools which help to assess the positive and negative impacts of a low-emission pathway for the country. Interview questions formed the basis for a series of model runs to obtain a better understanding of the implications of the energy efficiency pathway in Poland. The goal of the model run was to shed light on the macroeconomic impacts of investment in energy efficiency in Poland in the built environment.
Wytze van der Gaast
Research often focuses on creating and modelling hypothetical scenarios. However, public knowledge and opinions are crucial for the successful uptake of research findings. In this article, we explore how quantitative tools are used for producing scenarios, whereas qualitative tools are used to identify stakeholder preferences.
In the framework of the POLIMP project, a policy brief has been published on the role of social acceptance in the acceleration of clean technology deployment within the EU.
It is important to have a clear understanding of the relevant systems when designing pathways towards low emissions. An innovative tool has been designed specifically for the purposes of system mapping: Mapping Tool for Innovation Systems Evaluation (MATISE).
Interactions between EU climate and energy policies have been analysed based on France, Austria, Greece, and EU-level for policy interaction examples. The analysis resulted in 6 main findings.
Austria will add additional financial means to the existing policy framework to reach their target value for primary energy consumption of 1050 PetaJoule in 2020 (compared to 1120 PJ in 2013). The case study has analysed whether energy efficiency improvement policies lead to overlaps with policies at the level of provincial governments and what this could mean for the effectiveness and efficiency of the policies.