Transition pathways are compared to the land use domain of the Netherlands and Portugal. The land use domain analyses land systems and the changes within them and typically involves the analysis of land cover and land use. 4 main regimes were identified, three of which are common to both: agriculture, nature, and urban, and one which is different for each. The Dutch and Portuguese niches under study are all examples of regime transformation niches.
Articles
GHG emissions need to be reduced practically to zero by 2050. However, there are currently numerous coal-fired power stations around the world at different stages of construction, and if built and become active, their expected future emissions will make it difficult to reach the targets in the Paris Agreement. Carbon Capture and Storage could reduce future emissions, but its future availability is still highly uncertain.
Comparing the observed transition pathways in the agro-food domain in the Netherlands and Hungary investigates niche innovations from both countries and provides insight into the potential ways toward a sustainable and low carbon society. Differences and similarities between the countries can be explained by the following: societal issues, export vs. import, the government environment, the focus of policy, government involvement, and geographical context. Innovation is the best chance for direct progress to reduce the pressure.
An assessment of national, regional, and local needs for the implementation and improvement of energy efficiency policies in the EU was conducted regarding policymakers’ needs were identified and analysed to help Member States to implement useful and successful sustainable energy policies. A SWOT analysis was conducted for experiences in the development and implementation of energy efficiency policies at regional and local levels.
The poorest people still struggle to have access to sanitation and clean energy. However, as incomes rise in developing countries, access to electricity, clean cooking energy, water, and sanitation, also improves but not as quickly as income growth. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim to achieve universal access to clean energy, water, and sanitation by 2030. This study highlights the challenges of achieving SDGs, but also points to policy directions that could help.
Models are tools which help to assess the positive and negative impacts of a low-emission pathway for the country. Interview questions formed the basis for a series of model runs to obtain a better understanding of the implications of the energy efficiency pathway in Poland. The goal of the model run was to shed light on the macroeconomic impacts of investment in energy efficiency in Poland in the built environment.
Institutional, economic, and social contexts influence the formulation and implementation of climate policy instruments. Three categories of contextual factors that are especially relevant to climate change mitigation in EU policymaking: institutions and governance, innovation and investment and attitudes, behaviour, and lifestyle. Different factors or conditions may facilitate or hinder effective policy implementation as so much depends on the institutional, economic, and social contexts. In addition, not only international pressures but also local barriers.
The Paris Agreement requires the world to keep climate change below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, with an aim to stay below 1.5°C. The 1.5° target is particularly demanding and would require both major and rapid change in energy demand and consumption. A key element is to analyze Green House Gas Emissions of consumer-based options in the EU, such as food, buildings and transportation. The Carbon-Cap project explores the effects of applying different policy options.
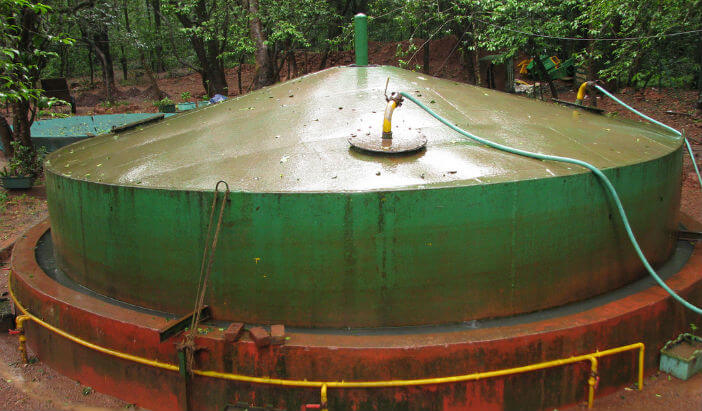
One of the 15 case studies of the EU-funded TRANSrisk project on transition pathways for climate change mitigation strategies is focused on the biogas sector in Indonesia. In this article, we explore the emissions reduction potential of a wider implementation of biogas in Indonesia.
Europe has taken a leading position in relation to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by adopting ambitious policies for the development and diffusion of renewable energy technologies. However, research and development (R&D) in new technologies is increasingly taking place on a global scale. This increasingly also involves the relocation of R&D and value-adding innovative activities to emerging economies, such as China, India and Brazil, by multinational companies (MNCs) from Europe.