How Earth System Models assess land-based carbon removal (AR, BECCS): carbon-cycle responses, and local climate side-effects; and how Integrated Assessment Models then asses socio-economic constraints that shape decision-ready deployment.
Agriculture / forestry
WATERAGRI aims to address critical challenges in agricultural water and nutrient management by developing scalable, farm-level solutions. The project focuses on improving water retention in soils and streams while optimizing […]
PREPSOIL focuses on restoring ecosystem services such as climate mitigation, water infiltration, and food production by addressing key challenges like desertification, carbon loss, erosion, and nutrient pollution. Central to its […]
EJP SOIL aims to transform agricultural practices by fostering sustainable soil management across Europe. Its primary goals include enhancing soil health to combat climate change impacts like droughts, compaction, and […]
LANDMARC’s final policy event is taking place in Brussels on 28 November 2024. The event will focus on the policy implications of Carbon Farming (CF), Carbon Capture and Storage/Utilization (CCS/CCU) and Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) technologies.
The UPSURGE project, led by BURST, focuses on urban Nature Based Solutions (NBS) for biodiversity and climate change. BeeOdiversity, a key partner, introduces the BeeOmonitoring tool, utilizing bees to gather environmental data. This innovative approach requires minimal effort from beekeepers and facilitates collaboration via an online dashboard. Past projects in Belgium show promising results in biodiversity and pollution reduction. Dr. Nguyen’s vision emphasizes integrating economic, environmental, and social aspects for sustainable change, aligning with NBS.
Throughout the centuries, people have been keen to find and discover new areas and exploit the natural resources associated with them. According to Margaret Kohn and Kavita Reddy (2017), the term colonialism describes the process of European settlement and political control over the rest of the world, including the Americas, Australia and parts of Africa and Asia.
Justice has long been central to geographic research but attention to the concept itself has been less explicitly theorized within the discipline. This article specifically traces the ways in which justice has been theorized within human geography.
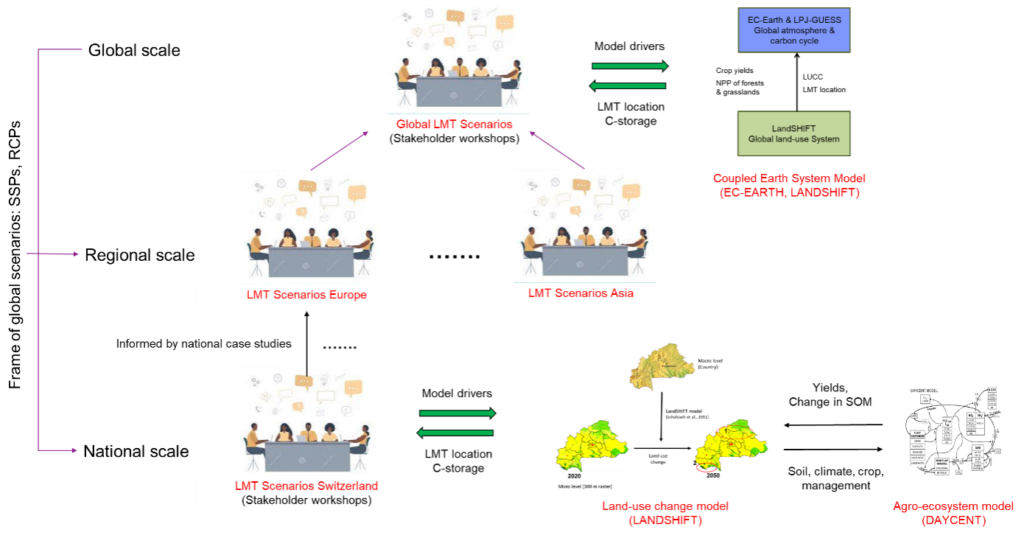
At LANDMARC, we are developing methods and instruments that non-researchers can use to reliably estimate how different land-use practices contribute to climate change mitigation. In our view, this can only be done by bringing in local knowledge at every stage of the research process. Here’s why.
Rather than trying to plant as many trees as possible, research coming out of the LANDMARC project suggests that it might be better to focus on planting fewer trees and managing them well, in a way that’s good for the underlying soil.
- 1
- 2